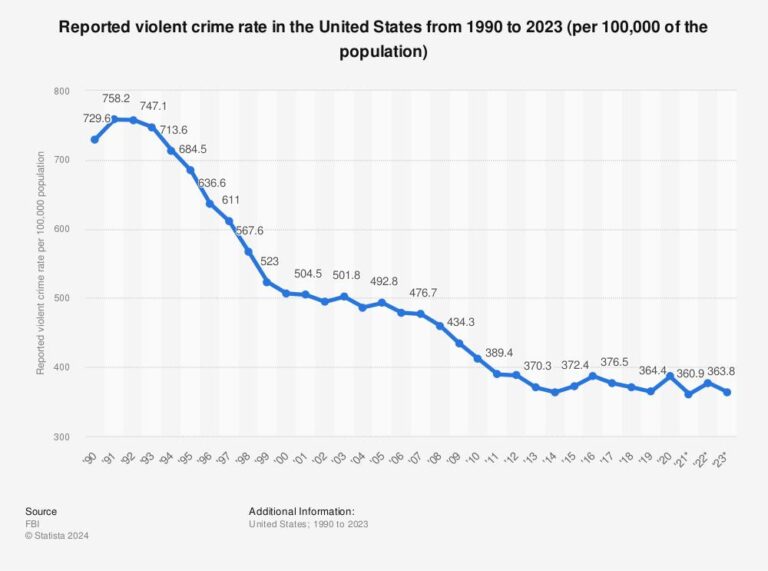
Preliminary data reveal that crime rates across the United States continue to decline, marking a sustained downward trend in recent years. According to the latest analysis from the Prison Policy Initiative, both violent and property crimes have decreased, challenging longstanding perceptions about rising crime. This ongoing shift has significant implications for policy discussions around criminal justice reform and public safety nationwide.
U.S. Crime Rates Show Consistent Decline Across Major Categories
Preliminary reports from law enforcement agencies and independent crime monitors indicate a sustained reduction in crime rates throughout the United States. Significant declines have been observed across major categories, including violent crime, property crime, and drug-related offenses. Experts attribute this downtrend to several factors such as enhanced community policing efforts, advancements in forensic technology, and increased social programs aimed at crime prevention.
Here is a brief overview of the latest crime statistics highlighting key areas of improvement:
- Violent Crime: Decreased by 7% compared to the previous year.
- Property Crime: Saw a 10% reduction, driven largely by fewer burglaries and vehicle thefts.
- Drug Offenses: Fell by 5%, partly due to targeted enforcement and community outreach.
| Crime Category | 2023 Rate (per 100,000) | Change from 2022 |
|---|---|---|
| Violent Crime | 350 | -7% |
| Property Crime | 1,200 | -10% |
| Drug Offenses | 450 | -5% |
Preliminary Data Reveals Regional Variations and Emerging Trends
While national crime rates continue their downward trajectory, the latest preliminary data uncovers notable disparities among different regions. The Northeast and Midwest have experienced the most significant reductions in violent crime, with some metropolitan areas reporting declines exceeding 15% compared to last year. In contrast, parts of the South and West show smaller decreases or relative stability, highlighting persistent challenges tied to local socio-economic dynamics and law enforcement resource allocation.
- Northeast: Sharp declines in aggravated assault and robbery.
- Midwest: Notable drop in property crimes, especially burglary.
- South: Mixed patterns, with some cities seeing upticks in specific offenses.
- West: Steady violent crime rates, but growing concerns over gun-related incidents.
| Region | Violent Crime Change (%) | Property Crime Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | -16% | -12% |
| Midwest | -10% | -18% |
| South | -3% | -5% |
| West | 0% | -7% |
Emerging trends further reveal the evolving nature of crime across the nation. Cyber-enabled offenses such as identity theft and fraud have surged, amplifying concerns within both urban and rural communities. Additionally, law enforcement agencies report an increasing incidence of domestic violence cases, underscoring the need for targeted support services and new preventative strategies. These shifts suggest that although traditional crime categories decline overall, criminal activity is diversifying and adapting in response to broader societal changes.
Experts Analyze Factors Contributing to the Sustained Drop in Crime
Analysts highlight a combination of societal and policy-driven factors as key drivers behind the ongoing reduction in crime rates across the United States. Among these, improved community policing initiatives and expanded access to social services stand out as crucial elements. Experts emphasize that investments in mental health resources and youth outreach programs have provided vulnerable populations with critical support, effectively disrupting pathways that often lead to criminal behavior.
Other notable contributors include:
- Technological advancements in surveillance and data analysis enhancing law enforcement effectiveness.
- Economic improvements that reduce financial desperation.
- Legislative reforms focused on decriminalization and alternatives to incarceration.
- Increased collaboration between local governments and community organizations.
| Factor | Impact on Crime Rate | Estimated Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Enhanced trust and prevention | 30 |
| Social Services Expansion | Supports at-risk groups | 25 |
| Economic Growth | Reduced economic motivators | 20 |
| Legislative Reforms | Alternative sentencing | 15 |
| Law Enforcement Tech | Improved crime detection | 10 |
Policy Recommendations Focus on Community Investment and Criminal Justice Reform
To sustain the ongoing decline in crime rates, experts emphasize the importance of strategic community investments. These recommendations include:
- Expanding access to quality education to address root causes of crime and promote social mobility.
- Increasing affordable housing initiatives to reduce homelessness and stabilize vulnerable populations.
- Enhancing mental health services to support individuals facing trauma and substance abuse issues.
Simultaneously, criminal justice reform remains a critical component of reducing incarceration rates without compromising public safety. Key policy changes advocated by reformers include:
- Reducing mandatory minimum sentences for nonviolent offenses to limit prison overcrowding.
- Promoting alternatives to incarceration such as restorative justice programs and community supervision.
- Implementing bias training and accountability measures in law enforcement to build trust between police and communities.
| Policy Area | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Community Education Programs | Lower recidivism through skill-building |
| Mental Health Services | Reduced emergency response calls |
| Sentencing Reform | Decreased prison population |
Concluding Remarks
As the latest figures underscore a continued decline in U.S. crime rates, preliminary data suggest that this trend may persist, offering a cautiously optimistic outlook for public safety. However, experts emphasize the need to address underlying social and economic factors to sustain and further these improvements. Policymakers and communities alike will be closely monitoring upcoming reports to inform strategies that promote long-term crime reduction and justice reform.