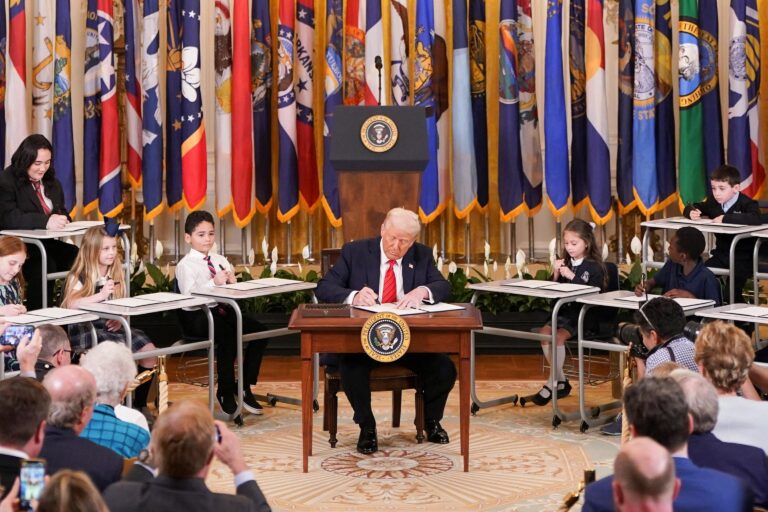
Former President Donald Trump’s proposal to close the U.S. Department of Education has sparked intense debate across the political spectrum. While the idea aligns with his broader agenda to reduce federal oversight and devolve authority to states, experts emphasize that dismantling a sprawling federal agency is a complex, prolonged process fraught with legal, logistical, and political obstacles. This article explores the practical challenges and implications of such a move, underscoring why eliminating the Education Department is far easier said than done.
Trump’s Proposal to Eliminate the Education Department Faces Legal and Political Hurdles
Efforts to dismantle the U.S. Department of Education face significant obstacles that extend beyond partisan debate. While the proposal aims to streamline federal oversight and reduce government spending, legal experts point out that abolishing a cabinet-level agency is a complex process requiring congressional approval, potential constitutional challenges, and extensive legislative restructuring. The education sector’s entwinement with both federal and state laws means any attempt to eliminate the department would trigger a prolonged policy overhaul involving myriad stakeholders.
Politically, the proposal is contentious, drawing sharp criticism from lawmakers, educators, and advocacy groups who emphasize the department’s role in ensuring equity and access to quality education nationwide. The following are some of the critical hurdles the proposal faces:
- Congressional Resistance: Bipartisan opposition could stall or block legislation needed to dissolve the department.
- Implementation Complexity: Transferring federal education programs to states could disrupt funding and oversight.
- Legal Challenges: Potential lawsuits regarding federal authority over civil rights and education standards.
- Public Backlash: Concerns about increasing disparities and reducing protections for vulnerable student populations.
The Potential Impact of Closing the Education Department on Federal Funding and Student Services
Eliminating the federal Education Department would send shockwaves through the intricate web of funding that supports schools across the nation. This agency administers billions of dollars annually, aimed at safeguarding equal access to education and bolstering underserved communities. Without a centralized body, states would face unprecedented challenges reallocating these funds efficiently, potentially widening educational disparities. Critical programs, such as Title I grants for low-income districts and IDEA funding for special education, might see delays or reductions, disrupting services vital to millions of students.
Beyond the financial implications, the retreat of the department could dilute oversight on key issues like civil rights compliance and educational standards. Local districts could lose the technical support and initiatives that help improve student outcomes. To illustrate, consider the following impacts:
- Reduced monitoring of discrimination and equity violations in schools.
- Fragmented administration of student loan programs, complicating repayment and forgiveness processes.
- Loss of research funding critical for developing innovative teaching methods.
| Program | Current Annual Federal Funding | Potential Risk if Department Closes |
|---|---|---|
| Title I Grants | $16.5 billion | Delayed distribution, impacting low-income schools |
| Individ. w/ Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) | $13 billion | Reduced oversight, service interruptions |
| Pell Grants | $30 billion | Administrative complexities, student confusion |
Experts Weigh In on Alternatives to Reforming Education Without Department Closure
Leading education policy experts emphasize that reforming the nation’s education system does not necessarily require shuttering the Department of Education. Many argue that incremental adjustments focused on empowering local districts and increasing school choice can yield significant improvements without dismantling the federal infrastructure. Strategies proposed include:
- Redirecting funds directly to schools to enhance accountability and transparency.
- Increasing support for innovative teaching methods through targeted grants.
- Strengthening collaboration between states to share best practices and reduce bureaucratic overhead.
Experts caution that the wholesale closure of a federal agency presents complex logistical and legal hurdles, which could disrupt services that millions of students rely on. Furthermore, the Department currently plays a pivotal role in enforcing civil rights laws and distributing financial aid. Below is a summary of alternative reform approaches evaluated by policymakers:
| Reform Approach | Potential Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Greater local control, tailored solutions | Risk of inequality among districts |
| Increased School Choice | More options for families, competitive improvement | Concerns over funding distribution |
| Federal Grant Reform | Targeted innovation, transparency | Complex implementation, oversight needed |
Strategies for Lawmakers to Address Education Reform While Navigating Bureaucratic Challenges
Lawmakers face an intricate web of bureaucratic hurdles when attempting to overhaul the nation’s education system. Streamlining policies requires more than political will—it demands a nuanced understanding of regulatory frameworks and stakeholder interests. One effective strategy involves fostering collaboration between federal, state, and local entities to build consensus and ensure smooth policy implementation. This approach allows for adaptive reforms that respect the autonomous structures already in place, reducing friction and promoting sustained change.
Additionally, prioritizing incremental changes over sweeping mandates can ease resistance within the Department of Education and its affiliated agencies. By targeting specific issues with measurable goals—such as enhancing funding transparency or revising curriculum standards—lawmakers can demonstrate tangible progress without triggering widespread bureaucratic pushback. Consider the comparative impact of reforms outlined in the table below, which highlights potential benefits and obstacles encountered during recent legislative efforts:
| Reform Focus | Benefits | Potential Bureaucratic Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Allocation Transparency | Increased accountability and public trust | Resistance from entrenched financial departments |
| Standardized Curriculum Updates | Improved educational consistency | Divergent state policies and local control issues |
| Teacher Professional Development | Enhanced classroom outcomes | Complex approval processes and union negotiations |
Insights and Conclusions
Closing the Department of Education, as proposed by former President Trump, presents a complex challenge that extends well beyond political rhetoric. While the idea appeals to certain constituencies seeking smaller federal government, the practicality of dismantling an entrenched agency with wide-ranging responsibilities is fraught with legal, logistical, and educational hurdles. As policymakers and stakeholders continue to debate the future role of the federal government in education, it remains clear that any effort to shutter the department will require careful consideration, substantial planning, and broad consensus—making it far easier said than done.