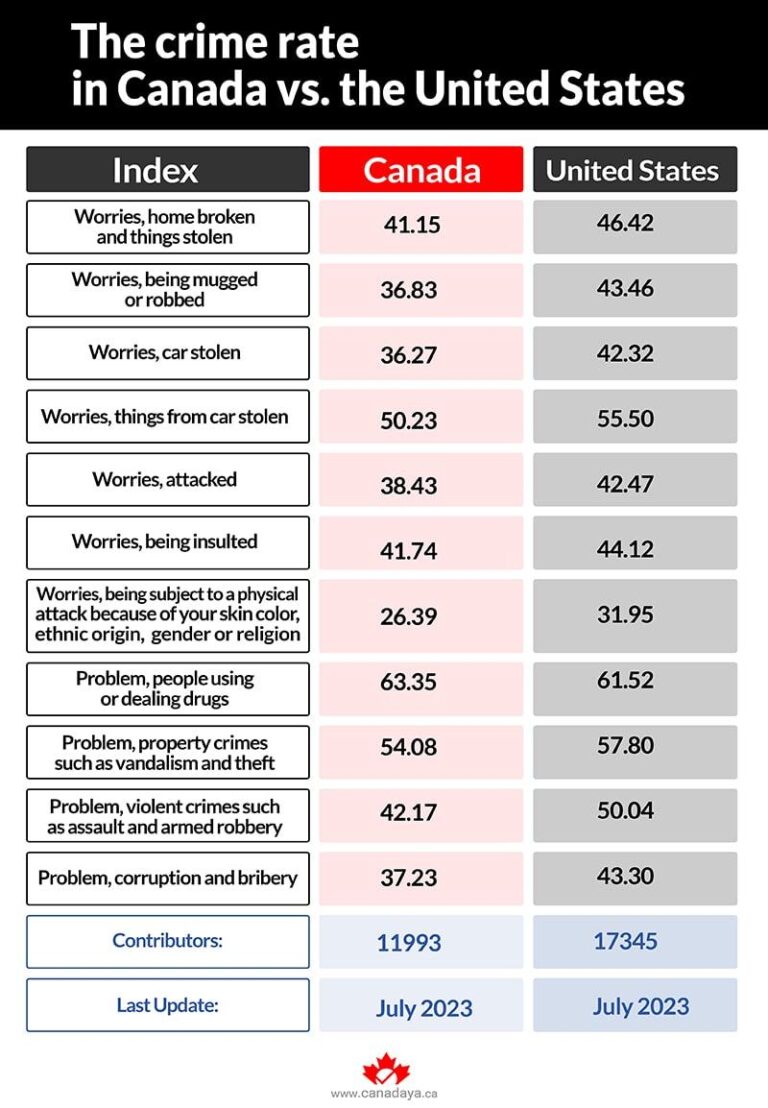
Recent analyses from the Fraser Institute have shed new light on the evolving landscape of crime in North America, drawing a detailed comparison between Canada and the United States. As both countries navigate shifting social and economic conditions, understanding their respective crime trends is critical for policymakers, law enforcement, and the public. This article delves into the latest data, exploring key differences and similarities in crime rates, types of offenses, and regional variations, offering a timely overview of public safety on either side of the border.
Comparing Crime Rates and Patterns Across Canada and the United States
Over the past decade, crime rates in both Canada and the United States have exhibited distinct trajectories, influenced by socio-economic factors and law enforcement strategies. While the U.S. continues to report higher rates of violent crimes such as homicides and armed assaults, Canada shows a relatively stable pattern, with modest fluctuations primarily in property-related offenses. Notably, urban centers in both countries experience concentrated impacts, with crime hotspots often correlating to areas facing economic challenges and systemic inequalities.
Key differences also emerge when examining the types of offenses most prevalent in each country:
- Canada: Property crimes, including theft and vandalism, tend to dominate the statistics, although violent crime rates have slightly increased in recent years.
- United States: Beyond property crimes, the U.S. faces higher instances of aggravated assaults and gun-related incidents, reflecting broader cultural and legislative disparities regarding firearms.
| Crime Category | Canada (per 100,000) | U.S. (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| Homicides | 1.8 | 5.0 |
| Robberies | 77 | 110 |
| Property Crimes | 1,950 | 2,200 |
| Assaults | 600 | 320 |
These trends underscore the importance of tailored policy responses. While Canada’s emphasis on community-based interventions appears to contribute to overall stability, addressing violent crime in the U.S. may require deeper engagement with violence prevention and gun control reform. As both nations continue to evolve, ongoing comparative analysis remains critical to enhancing public safety outcomes north and south of the border.
Economic and Social Factors Influencing Recent Crime Trends
Economic disparities remain a critical driver behind fluctuating crime rates in both Canada and the United States. In recent years, areas with pronounced income inequality and elevated unemployment have consistently reported higher incidents of property and violent crimes. The pandemic’s aftereffects further amplified these challenges, disproportionately impacting marginalized communities and fueling socio-economic stressors that correlate strongly with criminal activity. Notably, in both countries, younger populations facing limited economic opportunities have demonstrated an increasing presence in crime statistics, underscoring the urgent need for targeted social interventions.
Beyond economics, shifting social dynamics also play a significant role. Changes in family structure, urbanization rates, and access to education have created complex environments where crime can either proliferate or recede depending on local conditions. Critical social factors include:
- Community cohesion: Neighborhoods with strong social bonds tend to experience lower crime rates.
- Access to mental health services: Limited support can contribute to higher occurrences of substance abuse-related offenses.
- Policing and legislative reforms: Shifts in law enforcement strategies impact crime reporting and prevention effectiveness.
These interconnected elements demonstrate that tackling crime requires multidimensional strategies that address both the root economic inequalities and the evolving social fabric of North American societies.
| Factor | Canada (Impact) | United States (Impact) |
|---|---|---|
| Income Inequality | Moderate | High |
| Unemployment Rate | Stable but rising in urban centers | Higher and more volatile |
| Community Cohesion | Strong in suburban/rural areas | Varies widely; urban decline noted |
| Access to Mental Health Services | Improving but uneven | Limited, with disparities by region |
The Impact of Law Enforcement Strategies on Crime Reduction
Different law enforcement approaches have yielded distinctive results across North America. In Canada, community policing and preventive measures have been prioritized, focusing on building trust and engagement within neighborhoods. This strategy has contributed to a steady decline in violent crime rates, particularly in urban centers where partnership programs with social services target at-risk populations. Conversely, the United States has often emphasized a more aggressive, enforcement-heavy model, including “stop-and-frisk” policies and militarized responses. While these efforts have succeeded in reducing specific types of crime, they have also sparked debates over civil liberties and potential long-term social impacts.
Key factors influencing these outcomes involve the allocation of funding and the integration of data-driven technologies. Below is a comparison table outlining the principal strategies employed by law enforcement agencies in both countries and their measurable effects:
| Strategy | Canada | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Policing Focus | Community engagement and prevention | Enforcement and deterrence |
| Crime Rate Trend | Steady decline in violent crime | Mixed results, with local variance |
| Technology Use | Data analytics for targeted interventions | Surveillance and predictive policing |
| Public Reaction | Generally positive trust-building | Controversy over civil rights |
- Canada’s approach has emphasized transparency and collaboration, leading to greater community cooperation.
- U.S. strategies have often prioritized rapid response and high arrest rates, yielding short-term crime suppression.
- The effectiveness of each model continues to be influenced by social factors and evolving policy priorities.
Policy Recommendations for Enhancing Public Safety in Both Countries
Strategic investments in community policing and social services can bolster public safety by addressing root causes of crime in both Canada and the United States. Increasing funding for neighborhood-based law enforcement initiatives encourages stronger ties between officers and residents, fostering trust and more effective crime prevention. Additionally, expanding access to mental health resources and addiction treatment programs targets vulnerabilities that often lead to criminal behavior, reducing repeat offenses and easing pressure on the justice system.
Policy-makers should prioritize collaboration across jurisdictions to streamline data sharing and coordinate response efforts. Key areas for improvement include:
- Standardizing crime reporting systems to improve comparative analysis and trend identification.
- Implementing early intervention programs focused on at-risk youth to deter gang involvement and juvenile offending.
- Enhancing victim support services to improve recovery outcomes and encourage reporting.
| Policy Focus | Canada | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Enhanced local engagement programs | Focus on training and accountability |
| Early Intervention | Youth mentorship expansion | Nationwide juvenile justice reforms |
| Data Collaboration | Provincial-federal partnerships | Interstate task forces |
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the Fraser Institute’s analysis of recent crime trends highlights both convergences and divergences in the experiences of Canada and the United States. While certain categories of crime have shown comparable fluctuations, distinct socio-economic and policy factors continue to shape each country’s public safety landscape. As policymakers and communities seek effective solutions, understanding these nuanced patterns remains crucial for informed decision-making on both sides of the border.