California, long known for its sprawling urban centers and diverse population, often faces scrutiny over its crime rates. A recent analysis by Al Jazeera sheds light on how the state’s homicide figures compare to those in some southern U.S. states. Challenging common perceptions, the report explores whether California’s homicide rates are actually lower than those in parts of the South, sparking discussions about regional crime trends and the factors influencing public safety across America.
California’s Homicide Rates Compared to Southern States
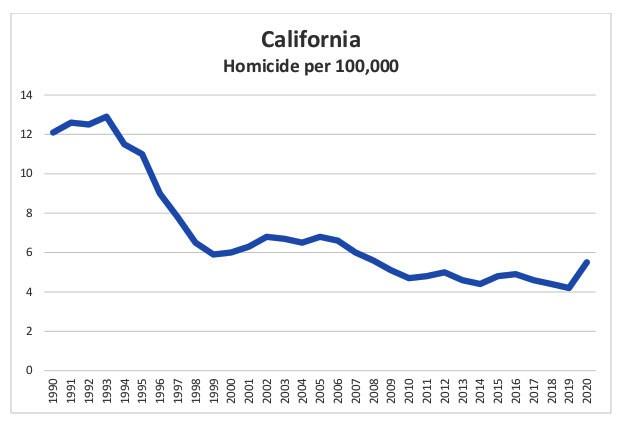
California, often perceived as a state grappling with high crime, actually reports homicide rates that compare favorably against several Southern states known for elevated violence levels. While California’s diverse urban centers face challenges, data indicates that states like Louisiana, Alabama, and Mississippi consistently register higher per capita homicide rates. This contrast highlights the complexity of regional crime dynamics where factors such as socioeconomic conditions, gun legislation, and law enforcement strategies play pivotal roles.
Key points in comparing homicide rates:
- California: Approximately 4.5 homicides per 100,000 residents (latest FBI data)
- Louisiana: Surpasses 11 homicides per 100,000 residents, among the highest nationwide
- Alabama: Around 8.5 homicides per 100,000 residents
- Mississippi: Close to 7.8 homicides per 100,000 residents
| State | Homicide Rate (per 100,000 residents) | Population (millions) |
|---|---|---|
| California | 4.5 | 39.2 |
| Louisiana | 11.3 | 4.6 |
| Alabama | 8.5 | 5.1 |
| Mississippi | 7.8 | 3.0 |
Factors Contributing to Regional Violent Crime Disparities
Regional disparities in violent crime, particularly homicide rates, stem from a complex interplay of socioeconomic, cultural, and systemic factors. Economic inequality remains a primary driver, with areas suffering from high unemployment, limited access to quality education, and insufficient social services often experiencing elevated violence rates. In contrast, states or regions that invest more in community programs and social infrastructure tend to report lower homicide incidences. Additionally, historical patterns of segregation and urban development play pivotal roles in shaping these crime landscapes.
Law enforcement strategies and criminal justice policies also substantially impact violent crime statistics. States with more aggressive policing tactics or higher incarceration rates may temporarily suppress violent crime, but they can also engender community distrust and long-term instability. Cultural factors, such as gun ownership prevalence and regional attitudes toward violence, further influence these disparities. Below is a simplified comparison table illustrating some of these contributing factors between California and select Southern states:
| Factor | California | Southern States (e.g., Louisiana, Mississippi) |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment Rate | 7.5% | 9.2% |
| Educational Attainment (High School Grad %) | 83% | 76% |
| Gun Ownership Rate | 22% | 45% |
| Incarceration Rate (per 100,000) | 380 | 700 |
Impact of Law Enforcement Strategies and Community Programs
California’s approach to reducing homicide rates contrasts sharply with some southern states, thanks in large part to its multifaceted law enforcement strategies and community-centric programs. Authorities have increasingly emphasized data-driven policing and inter-agency collaboration, which allow for targeted interventions in high-crime areas. Programs such as crisis intervention teams and gang prevention initiatives work hand-in-hand with traditional policing methods, fostering trust between residents and officers. This dual approach has been critical in disrupting cycles of violence and enabling safer neighborhoods.
Community programs complement law enforcement efforts by addressing underlying social issues linked to violence. Investments in youth mentorship, mental health access, and job training create pathways away from crime for vulnerable populations. Key elements include:
- Neighborhood watch partnerships enhancing local vigilance
- After-school activities providing safe spaces for at-risk youth
- Reentry programs supporting formerly incarcerated individuals
| Strategy | Primary Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data-Driven Policing | Hotspot Identification | Reduced Crime by 15% |
| Youth Mentorship Programs | Engagement & Prevention | Lowered Gang Recruitment |
| Mental Health Services | Crisis Intervention | Decreased Violent Incidents |
Policy Recommendations to Reduce Homicide Rates Nationwide
Addressing the stark disparities in homicide rates across states calls for targeted and multifaceted policy approaches. Community-based violence interruption programs have shown promising results by leveraging local influencers to mediate conflicts before they escalate. These initiatives, combined with strategic investments in mental health services and substance abuse treatment, can mitigate some underlying drivers of violence. Scaling such programs nationally requires both federal support and cooperation with state and local governments to adapt interventions to local contexts.
In addition to community strategies, reforming the criminal justice system to focus on rehabilitation rather than purely punitive measures can reduce recidivism rates and long-term violence. Policies should also emphasize economic opportunities and education in high-risk neighborhoods, as economic disadvantage correlates strongly with higher homicide rates. Consider this simplified comparison of key policy impacts on homicide reduction measured in pilot programs:
| Policy Intervention | Homicide Reduction (%) | Implementation Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Community Violence Interruption | 25% | 2 years |
| Mental Health & Substance Abuse Services | 18% | 3 years |
| Educational & Economic Opportunities | 22% | 4 years |
| Criminal Justice Rehabilitation Programs | 20% | 3 years |
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, while California is often perceived as having higher crime rates due to its large population and urban centers, the data reveals that some Southern states report higher homicide rates per capita. This contrast highlights the complexity of regional crime dynamics and the importance of examining local social, economic, and policy factors when addressing public safety. As discussions around crime and policy continue nationwide, understanding these nuanced differences remains crucial for informed debate and effective solutions.