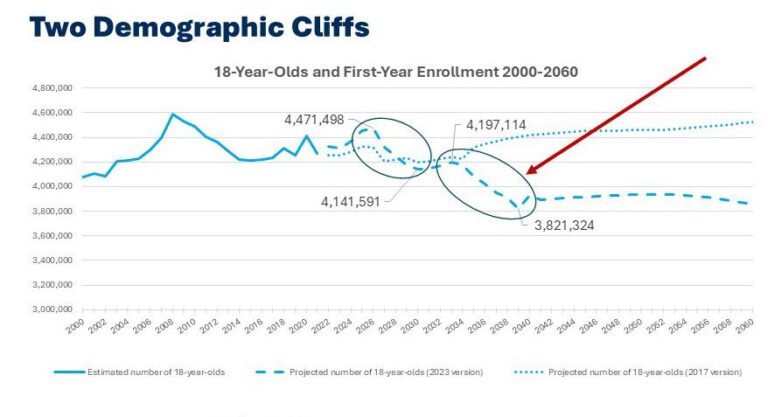
A significant shift is on the horizon for higher education in the United States, as experts warn of a looming “demographic cliff” that threatens to shrink college enrollments and reduce the number of graduates in the coming years. NPR reports that declining birth rates and changing population patterns are driving a downturn in the pool of traditional college-age students, presenting a critical challenge for universities, policymakers, and the workforce. This demographic shift could reshape the landscape of American higher education and have far-reaching implications for economic growth and innovation.
Declining Birth Rates Create Challenges for Higher Education Enrollment
As birth rates continue to fall across much of the country, higher education institutions face a shrinking pool of prospective students. This demographic shift poses significant hurdles for colleges and universities that rely on steady or increasing enrollment numbers. With fewer high school graduates, competition intensifies, pushing schools to innovate recruitment strategies and reconsider program offerings to maintain both enrollment and revenue. The ripple effects extend beyond just the campuses, influencing local economies and workforce pipelines dependent on a steady flow of college-trained professionals.
Key factors shaping this emerging challenge include:
- Geographic disparities: Some regions experience sharper declines, forcing regional schools to adapt differently than national universities.
- Financial pressures: With diminishing student numbers, institutions face budget constraints that could impact faculty hiring and campus services.
- Changing demographics: Shifts in racial and ethnic compositions affect recruitment and retention strategies.
| Year | Projected High School Graduates (millions) | Enrollment Impact (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 3.7 | 0 |
| 2027 | 3.4 | -8 |
| 2030 | 3.1 | -16 |
Universities Brace for Budget Shortfalls as Student Numbers Drop
Across the nation, higher education institutions are confronting a stark reality: enrollment rates are plunging due to shifting demographic trends. As birth rates decline and the college-age population shrinks, universities face a tightening financial squeeze that threatens both program offerings and staffing levels. Many institutions, especially smaller regional colleges, are already adjusting their budgets, cutting back on faculty hiring, and scaling down campus services to brace for the impact.
Key challenges include:
- Declining tuition revenue from fewer incoming students
- Increased competition for a smaller pool of applicants
- Pressure to innovate recruitment and retention strategies
- Potential program consolidations and closures
| Region | Projected Enrollment Decline (%) | Expected Budget Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Midwest | 15% | Moderate |
| Northeast | 20% | Severe |
| South | 10% | Mild |
| West | 12% | Moderate |
Experts warn that without strategic adaptation, the cascading effects may affect overall workforce development and economic stability. Universities are exploring cross-sector collaborations, enhanced online offerings, and targeted scholarships to mitigate the fallout. However, the challenge remains formidable as the demographic shifts signal a long-term realignment in higher education’s landscape.
Innovative Recruitment Strategies Aim to Attract a Shrinking Pool of Applicants
As the number of college students continues to decline nationwide, companies are forced to rethink their recruitment playbooks to capture the attention of a dwindling talent pool. Traditional hiring methods like generic job postings and mass college fairs are quickly becoming ineffective. Instead, organizations are adopting more personalized, tech-savvy strategies — including targeted social media campaigns, virtual internships, and AI-driven candidate matching — aimed at both engaging passive applicants and maximizing outreach efficiency.
These innovative approaches also come with a growing emphasis on diversity and inclusion, as employers recognize the need to tap into underrepresented groups to offset the shrinking graduate population. The table below highlights some of the key recruitment tactics currently gaining traction and their main benefits:
| Strategy | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Career Events | Remote engagement of candidates | Broader reach, cost savings |
| AI-Powered Screening | Efficient candidate filtering | Faster hiring, reduced bias |
| Targeted Social Campaigns | Engage niche applicant groups | Increased quality of leads |
| Campus Micro-Internships | Short-term practical experience | Stronger talent pipelines |
Policy Recommendations Focus on Expanding Access and Retention Efforts
To counter the expected decline in college enrollments, experts emphasize the urgent need for targeted policies that broaden educational access while enhancing student retention. Proposed measures prioritize increased funding for scholarships and grants aimed at economically disadvantaged populations, expanding dual-enrollment opportunities for high school students, and the development of flexible learning pathways such as online and part-time programs. These initiatives are designed to make post-secondary education more adaptable and inclusive, especially for non-traditional students who juggle work and family responsibilities.
- Expand financial aid programs to alleviate economic barriers
- Invest in early college outreach to build pathways from high school
- Enhance retention support services, including mental health and tutoring
- Promote innovative delivery models such as hybrid and evening classes
Retention remains equally critical in addressing the demographic cliff, with colleges urged to implement comprehensive support systems that tackle academic, social, and financial challenges. Institutions are encouraged to adopt data-driven approaches to identify at-risk students early and provide personalized interventions. Below is a snapshot of commonly adopted retention strategies across various types of institutions, highlighting where resources might be most effectively directed.
| Retention Strategy | Percentage of Colleges Implementing | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Advising Enhancements | 78% | Improved course planning and goal tracking |
| Mental Health & Wellness Programs | 65% | Reducing student stress and anxiety |
| Early Alert Systems | 54% | Identifying struggling students early |
| Peer Mentoring | 49% | Building community and social support |
To Wrap It Up
As the nation confronts this looming demographic cliff, the ripple effects on higher education, the workforce, and the broader economy are becoming increasingly clear. With fewer college-bound students entering campuses and a subsequent decline in graduates, institutions must adapt to shifting enrollment patterns and reassess strategies for sustainability. Policymakers and educators alike face mounting pressure to address these changes proactively to ensure that the future of American higher education remains robust, equitable, and aligned with evolving societal needs. The coming years will be pivotal in determining how the country navigates this unprecedented demographic challenge.