In 2023, the landscape of violent crime in the United States continues to reflect persistent racial disparities, with murder victimization rates varying significantly across different demographic groups. According to the latest data compiled by Statista, patterns in homicide victims by race reveal critical insights into broader social and economic challenges faced by communities nationwide. This article explores these statistics to provide a clearer understanding of the ongoing impact of violence in the U.S., highlighting the urgent need for targeted interventions and policy responses.
Murder Victims by Race in the United States Analyzing 2023 Trends and Data
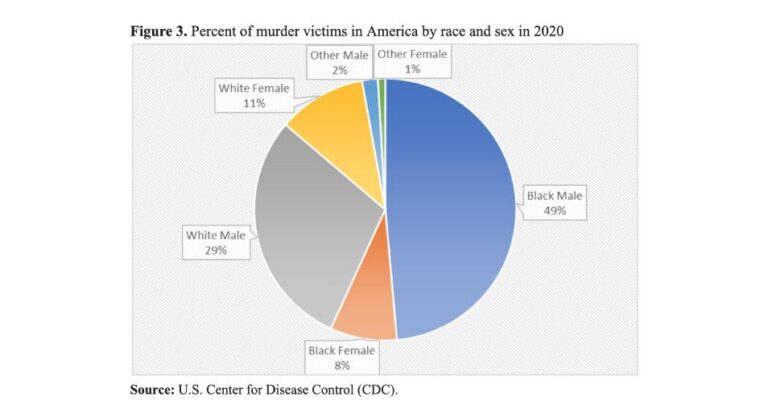
Data from 2023 highlights stark disparities in the racial composition of murder victims across the United States, reflecting enduring social and systemic issues. African Americans continue to bear a disproportionate burden, accounting for approximately 55% of all homicide victims despite representing just around 13% of the national population. Meanwhile, White victims comprise nearly 40%, and other racial groups make up a smaller fraction. These figures underscore the ongoing challenges related to community safety, economic disparity, and access to justice that remain critical areas for targeted intervention and policy reform.
Breaking down the statistics reveals key trends worth noting:
- Young adults between 18-34 years old represent the largest demographic among victims across all races.
- Urban centers with higher poverty rates continue to experience elevated murder rates, particularly affecting minority communities.
- Data suggests a subtle but growing increase in homicides involving Hispanic victims, highlighting shifting demographic patterns nationwide.
| Race | Percentage of Total Victims | Estimated Count (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| African American | 55% | 5,500 |
| White | 40% | 4,000 |
| Hispanic | 4% | 400 |
| Other | 1% | 100 |
Disparities in Victimization Rates Exploring Socioeconomic and Demographic Factors
When examining the disparities in victimization rates, it becomes evident that socioeconomic and demographic factors dramatically influence who is most affected by homicide in the U.S. Communities with lower median income levels often experience higher rates of violent crime, compounded by limited access to resources such as education, employment, and community support programs. Additionally, demographic variables such as age and gender intersect with race, further shaping victimization. Young males in economically disadvantaged urban neighborhoods, particularly those identifying as Black or Hispanic, constitute a prominently vulnerable group. These patterns reflect systemic inequalities that stretch beyond individual circumstances, underscoring the need for targeted policy interventions.
Addressing these disparities requires a nuanced understanding of the contributing factors. Here are some critical socioeconomic and demographic contributors:
- Economic Instability: High unemployment and poverty rates correlate strongly with increased homicide exposure.
- Educational Attainment: Lower access to quality education limits opportunities and may increase susceptibility to violence.
- Community Infrastructure: Neighborhoods suffering from disinvestment and inadequate law enforcement presence report higher victimization.
- Age and Gender: Younger men, particularly those aged 15–34, represent a disproportionate share of homicide victims.
| Factor | Impact on Victimization | Example Group |
|---|---|---|
| Median Income | Higher victim rates in lower income areas | Black urban males |
| Education | Lower attainment linked to increased risk | Hispanic youth |
| Age | Younger individuals face greater threat | 15–34 year-old males |
Impact of Regional Variations on Murder Victims by Race
The geographic disparities across the United States significantly shape the racial profile of murder victims. Urban centers, especially in the South and Midwest, report disproportionately high numbers of homicide cases involving Black victims, a reflection of economic, social, and systemic challenges unique to those regions. Conversely, areas in the West and Northeast tend to show a relatively higher percentage of Hispanic victims, influenced by demographic concentrations and regional migration patterns. These regional nuances underscore how localized factors such as poverty, community infrastructure, and law enforcement engagement contribute to the varying racial impact of violent crime.
Examining the data reveals clear patterns in victimization rates, emphasizing the importance of targeted policy responses. For instance:
- Southern States: Higher rates of violence affecting Black communities, highlighting systemic disparities.
- Western States: Greater representation of Hispanic victims, paralleling local demographic growth.
- Midwestern Cities: Notable spikes in young Black male victims, often linked to urban poverty zones.
| Region | Predominant Victim Race | Percentage of Total Murders |
|---|---|---|
| South | Black | 48% |
| West | Hispanic | 35% |
| Northeast | White | 40% |
Policy Recommendations to Address Racial Inequities in Violent Crime Prevention
Addressing racial disparities in violent crime prevention requires a multi-faceted approach rooted in community engagement and systemic reform. Investment in education and economic opportunities within marginalized communities can help mitigate the conditions often linked to higher victimization rates. Policy efforts should prioritize:
- Expanding access to quality schooling and vocational training
- Creating sustainable employment programs
- Supporting affordable housing initiatives
Additionally, law enforcement strategies must be restructured to foster trust and transparency. Implementing community policing models alongside independent oversight can reduce tensions and improve cooperation. Key recommendations include:
- Mandatory bias and de-escalation training for officers
- Enhanced data collection on race-specific crime statistics
- Community-led violence interruption programs
| Policy | Target Area | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Empowerment Grants | Urban Communities | Reduced crime through job creation |
| Community Policing Initiatives | High-Violence Neighborhoods | Increased public trust |
| Independent Oversight Boards | Law Enforcement Agencies | Enhanced accountability |
In Conclusion
In summary, the 2023 data on murder victims by race in the U.S. underscores persistent disparities that continue to challenge policymakers, law enforcement, and communities alike. As the nation grapples with addressing the underlying causes of violence, these statistics serve as a crucial reminder of the urgent need for targeted interventions and comprehensive strategies. Moving forward, a data-driven approach will be essential in crafting effective solutions to reduce homicide rates and promote safety for all Americans.