Analyzing the Economic and Cultural Influence of International Students on U.S. Higher Education
Financial Vulnerabilities Linked to High International Student Enrollment
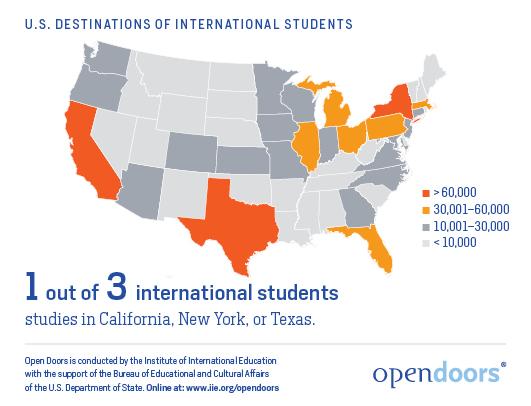
U.S. universities have increasingly depended on international students as a crucial revenue source and a means to enhance campus diversity. Yet, institutions where foreign students make up more than 30% of the student population often face significant financial risks. Abrupt shifts in global diplomacy, visa policies, or public health crises—such as the COVID-19 outbreak—can drastically reduce international enrollment, jeopardizing these schools’ financial health.
Key contributors to this economic fragility include:
- International students typically pay premium tuition fees, which help subsidize other university expenses.
- Overreliance on a narrow international student base increases susceptibility to enrollment volatility.
- Universities incur extra costs providing specialized services like visa guidance, language support, and cultural integration programs.
| University | International Student Ratio | Primary Region of Origin | Dependence on Tuition Revenue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lakeview University | 42% | South Asia | 50% |
| Coastal Tech College | 35% | North Africa | 46% |
| Greenfield State University | 31% | Europe | 43% |
International Students as Catalysts for Campus Diversity and Academic Innovation
The increasing influx of international students is transforming the cultural fabric and academic environment of U.S. universities. Campuses with a high proportion of foreign students enjoy enriched cultural exchanges that stimulate diverse viewpoints in classrooms, research collaborations, and extracurricular activities. This multicultural environment broadens global perspectives for all students but also demands that institutions tailor their resources to meet the distinct needs of international learners.
In response, many universities have launched new academic offerings and support mechanisms. These include enhanced language acquisition programs, interdisciplinary courses emphasizing global issues, and career services designed to align with international students’ goals. The following table showcases universities that have successfully integrated global trends into their academic frameworks and international partnerships:
| University | International Student Share | Recent Academic Developments | Global Partnerships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summit Ridge University | 45% | Global Policy Studies Minor, Advanced ESL Courses | Collaborations in 20 Countries |
| Harborview Institute | 38% | International Business Track, Expanded Exchange Programs | Alliances in 25 Countries |
| Evergreen Valley University | 50% | Cross-Cultural Psychology, International Environmental Policy | Networks in 15 Countries |
- Curricula are increasingly shaped by the diverse academic backgrounds and cultural experiences of international students.
- Robust support services are critical to ensuring academic success and retention among foreign students.
- International collaborations expand research horizons and foster cross-cultural understanding.
Strategies to Mitigate Financial Reliance on International Tuition
To lessen financial dependence on international tuition, universities are implementing diverse approaches. One key tactic involves expanding recruitment beyond traditional hubs like China and India to emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America. This geographic diversification helps cushion enrollment against geopolitical and economic uncertainties.
Concurrently, institutions are intensifying efforts to attract domestic students by enhancing financial aid packages and retention initiatives. The rise of online and hybrid education models also broadens access, appealing to working adults and non-traditional learners. Moreover, universities are developing academic programs aligned with regional labor market demands, thereby increasing appeal to in-state and neighboring state students. Collectively, these measures contribute to a more balanced and sustainable financial model.
Policy Recommendations to Strengthen Support for International Students and Institutional Resilience
Fostering a supportive atmosphere for international students necessitates comprehensive orientation and continuous assistance. Universities should offer programs addressing cultural adjustment, academic expectations, and legal complexities, including language tutoring, mental health resources, and workshops on U.S. immigration policies. Establishing mentorship networks that connect international students with alumni and local community members can further enhance social integration.
From a policy perspective, government agencies can facilitate smoother visa application and renewal processes and expand post-graduation employment opportunities. Funding initiatives that encourage research collaborations involving international students can leverage their diverse insights to drive academic innovation. The table below summarizes actionable recommendations for key stakeholders:
| Stakeholder | Suggested Initiative | Anticipated Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Universities | Create multilingual support centers | Improved retention rates and student satisfaction |
| Federal Government | Streamline visa processing and renewals | Reduced administrative delays |
| Local Communities | Develop cultural exchange and mentorship programs | Enhanced social cohesion and student well-being |
Conclusion: The Ongoing Role of International Students in U.S. Higher Education
The shifting patterns of international student enrollment continue to profoundly affect the financial stability and cultural vibrancy of U.S. colleges and universities. Understanding which institutions are most reliant on this demographic offers critical insights into enrollment trends and strategic planning. As educators and policymakers navigate these complexities, international students will remain pivotal in shaping the future trajectory of American higher education and its global engagement.