As concerns about public safety dominate headlines and community conversations, the question on many minds is clear: Does the United States currently face a crime crisis? Despite data showing fluctuating crime rates over the years, public perception often leans toward the belief that crime is steadily increasing. In this article, USA Today examines the complex factors behind crime statistics, explores why crime seems to be on the rise in the public eye, and analyzes what the numbers‚ÄĒand the stories behind them‚ÄĒreally reveal about safety in America today.
Understanding the Current State of Crime in the United States
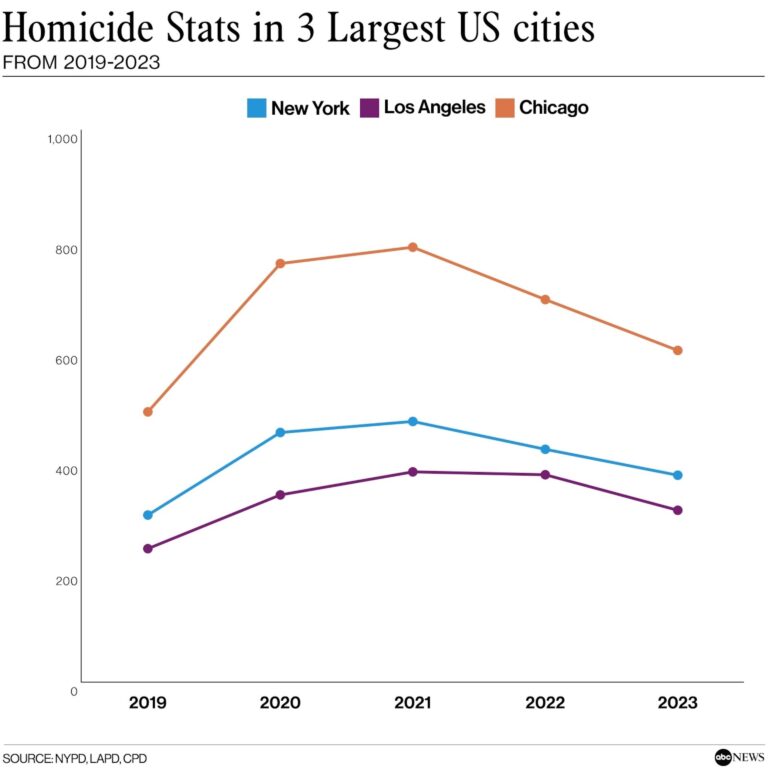
Crime statistics in the United States paint a complex picture, often fueling debates about whether the nation is facing an unprecedented crime surge. Recent data from the FBI and other law enforcement agencies reveal a nuanced trend rather than a uniform increase. While certain categories, such as violent crimes and homicides, have seen fluctuations‚ÄĒsometimes spiking in metropolitan areas‚ÄĒother crime types, including property offenses, have generally declined or stabilized. It’s important to recognize that these numbers can be influenced by multiple factors including changes in policing strategies, economic conditions, and community engagement efforts.
Several key elements contribute to the perception that crime is always on the rise:
- Media coverage: Sensationalized reporting often focuses on violent incidents, overshadowing broader trends.
- Reporting improvements: Enhanced crime reporting systems mean more data is captured today than in previous decades.
- Localized surges: Certain cities experience brief periods of increasing crime, impacting national discussions.
- Socioeconomic factors: Issues such as poverty and unemployment can temporarily affect crime rates in specific regions.
| Crime Type | Trend (Last 5 Years) | Notable Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Homicides | ‚ÜĎ Fluctuating with spikes | Large cities, Midwest |
| Burglary | ‚Üď Steady decline | Nationwide |
| Motor Vehicle Theft | ‚ÜĎ Slight increase | Western states |
Factors Behind the Perception of Rising Crime Rates
The feeling that crime is spiraling out of control is often fueled by several key influences beyond just the raw statistics. Media coverage plays a pivotal role, focusing disproportionately on violent incidents and sensational stories that captivate audiences but may distort the overall picture. This phenomenon, known as “crime news bias,” leads to a public perception that crimes are more frequent and severe than actual data suggests. Social media amplifies this effect, as viral videos and personal testimonies create an immediate, emotionally charged experience that feels more representative than it truly is.
Additionally, demographic and societal changes contribute to the perception of rising crime. Urbanization, economic disparities, and shifts in population density can create localized spikes in crime that attract widespread attention, even as national or state-level crime rates remain stable or decline. Moreover, improvements in data collection and reporting protocols mean that more incidents are recorded than in previous decades, complicating direct comparisons over time.
| Factor | Impact on Perception |
|---|---|
| Media Coverage | Focus on violent crime heightens fears |
| Social Media | Viral sharing intensifies emotional response |
| Reporting Improvements | More incidents officially documented |
| Urban Demographics | Localized crime tends to stand out |
- Fear and perception: Often influenced more by what’s reported than by actual crime rates.
- Data complexity: Modern crime statistics reflect broader reporting, not necessarily increases.
- Localized vs. National: Spikes in certain areas can skew the overall sense of safety.
Analyzing Data Trends Versus Media Narratives
When examining public perception of crime trends, it becomes evident that media narratives often influence the way the issue is framed, sometimes outpacing or even distorting the actual data. Headlines emphasizing spikes in violent crime, sensational acts, or increasing lawlessness capture attention, creating a sense of urgency and crisis. However, a deeper dive into crime statistics reveals a more nuanced picture. For example, while certain cities may experience short-term increases in specific crime categories, national data over recent decades have shown overall declines or stabilization in many crime rates. This discrepancy suggests that the storytelling in news outlets can amplify isolated incidents or trends, which may not reflect broader realities.
The divergence between data trends and media portrayal is further highlighted when considering the role of real-time reporting and social media amplification. News outlets often highlight violent or unusual crimes due to their immediate impact and shareability, overshadowing more common, less dramatic offenses that have remained steady or decreased. Additionally, the complexity of crime statistics ‚ÄĒ influenced by reporting practices, law enforcement strategies, and socio-economic factors ‚ÄĒ is rarely parsed out in media coverage, leading to oversimplified narratives. The following table contrasts key crime metrics with typical media focus areas:
| Crime Metric | Recent Data Trend | Common Media Emphasis |
|---|---|---|
| Violent Crime Rates | Stable or declining nationally | Isolated spikes in violent incidents |
| Property Crimes | Gradually decreasing over years | Sensational burglaries or thefts |
| Homicide Rates | Fluctuating regionally but generally lower than past decades | Focus on high-profile murders |
- Data complexity: Crime figures must be interpreted within context.
- Media influence: Sensational or dramatic stories drive public perception.
- Social impact: Fear of crime often rises even when statistics show stability.
Policy Measures and Community Strategies to Address Crime Effectively
To counteract rising crime rates, policymakers are increasingly adopting a multifaceted approach that balances enforcement with prevention. Key measures include strengthening community policing efforts, improving firearm regulations, and expanding funding for mental health services. These initiatives emphasize collaboration between law enforcement agencies and local organizations to build trust and promote transparent communication. Investment in technology, such as predictive analytics, also plays a vital role in directing resources efficiently and facilitating rapid response to hotspots.
Community-centered programs have demonstrated notable success by addressing root causes like poverty, unemployment, and education gaps. Effective strategies often involve:
- Youth engagement projects to deter gang involvement
- Neighborhood watch groups coupled with local surveillance upgrades
- Accessible rehabilitation and reentry services for former offenders
- Social services collaboration to support vulnerable populations
| Policy Measure | Community Benefit | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Improved trust and cooperation | High |
| Gun Control Legislation | Reduced firearm-related incidents | Medium |
| Youth Engagement Programs | Lowered gang recruitment rates | High |
| Mental Health Services | Preventive care and crisis intervention | Medium |
In Conclusion
In sum, the question of whether the U.S. is facing a true crime crisis is layered and complex. While some statistics point to increases in certain types of crime, broader data and contextual factors reveal a more nuanced reality. Understanding the interplay of social, economic, and systemic influences is key to addressing public concerns and shaping effective policies. As the national conversation continues, it remains critical to rely on accurate information and comprehensive analysis rather than perception alone.