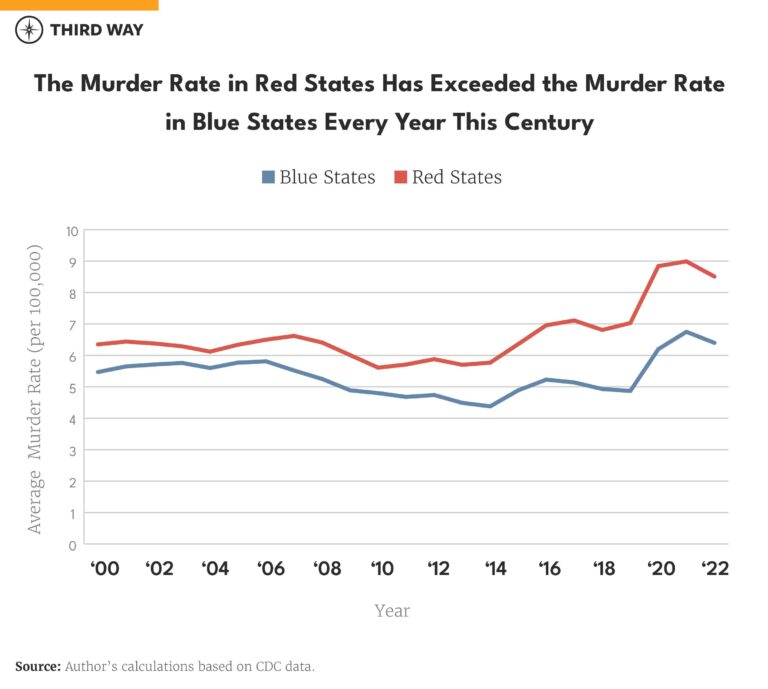
As debates over crime rates intensify in the United States, a recurring argument centers on whether cities governed by Democratic leaders experience higher levels of criminal activity. This article from dw.com takes a closer look at the data and investigations behind these claims, aiming to separate political rhetoric from factual evidence. By analyzing crime statistics, examining socio-economic factors, and comparing trends across multiple urban centers, the report seeks to provide a clearer picture of the complex relationship between city governance and public safety.
Crime Trends in Democrat-led Cities Examined Against National Data
Recent analyses of crime statistics from various federal databases highlight significant regional variations that challenge common perceptions about crime rates in Democrat-led urban areas. While some large cities governed by Democrats report higher violent crime numbers, these figures often correlate strongly with factors such as population density, economic disparity, and historical crime patterns rather than party governance alone. For example, cities with expansive public transit systems and larger homeless populations tend to experience more incidents of property crime and violence, independent of political leadership.
When juxtaposed with national averages, several Democrat-led cities exhibit crime rates that are on par with or below the overall U.S. figures in specific categories. The table below summarizes violent crime rates per 100,000 inhabitants in select Democrat-led cities compared to the national average, illustrating this nuanced landscape:
| City | Violent Crime Rate | National Average |
|---|---|---|
| Seattle, WA | 622 | 398 |
| New York City, NY | 461 | |
| Chicago, IL | 891 | |
| Los Angeles, CA | 732 |
- Socioeconomic conditions: Poverty and unemployment remain key drivers of crime across cities regardless of political leadership.
- Police funding and strategies: Variations in law enforcement resources and policies shape local crime dynamics significantly.
- Community programs: Investment in social outreach and public health initiatives correlates with reductions in specific crime categories.
Factors Influencing Crime Rates Beyond Political Leadership
Crime rates are shaped by a complex interplay of socioeconomic and environmental factors, far beyond the scope of political leadership alone. Variables such as poverty, unemployment, and educational disparities often serve as critical determinants of a city’s crime dynamics. For instance, neighborhoods grappling with economic hardships may experience higher incidences of crime due to limited access to resources and opportunities. Additionally, factors like population density and urban infrastructure directly impact how crime is manifested and perceived within communities, making any simplistic correlation with political leadership potentially misleading.
Other crucial contributors include community policing strategies, local law enforcement funding, and social services availability. The following table illustrates a simplified comparison of three influential factors across various metropolitan areas:
| Factor | High Crime City | Low Crime City |
|---|---|---|
| Poverty Rate | 28% | 10% |
| Unemployment Rate | 9.5% | 3.2% |
| Police Officers per 1,000 Residents | 2.4 | 4.1 |
These multifaceted influences underscore the importance of analyzing crime within a broader societal context‚ÄĒwhere political labels serve as only one part of a much larger picture. Understanding this complexity is crucial for devising effective public safety policies that address root causes rather than merely symptom management.
Impact of Socioeconomic Conditions and Policing Strategies
Crime rates in cities often correlate more strongly with socioeconomic factors than with political leadership. Areas plagued by poverty, unemployment, and inadequate education frequently experience higher instances of crime. These underlying conditions create environments where criminal activity can thrive due to limited opportunities and social unrest. Therefore, attributing crime trends solely to the political party of city leadership oversimplifies a deeply complex issue.
Policing strategies employed by cities also heavily influence crime statistics. Some Democrat-led cities have implemented reforms focused on community engagement and de-escalation, aiming to rebuild trust between law enforcement and residents. However, these approaches may result in short-term increases in certain crimes due to changes in enforcement tactics. Below is a comparison of typical policing strategies and associated outcomes in urban areas:
| Policing Strategy | Focus | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Building trust, crime prevention | Improved relations; fluctuating crime rates |
| Zero Tolerance | Strict enforcement, deterrence | Short-term crime drop; possible civil unrest |
| De-escalation Training | Reducing use of force | Lower violence complaints; challenges in certain crimes |
- Economic disparity often outpaces political impact on crime statistics.
- Policing methods can cause fluctuations in crime data independent of governance.
- Community trust remains a critical factor in sustainable crime reduction efforts.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing Urban Crime Effectively
To confront the complexities of urban crime, policymakers must embrace a multifaceted approach that transcends political affiliation or simplistic blame. Evidence underscores that investments in community-oriented policing and social support programs significantly reduce crime rates. These initiatives include increased funding for mental health services, youth engagement activities, and improved neighborhood infrastructure, all of which address root causes rather than symptoms. A strict law enforcement-only strategy often fails to yield sustainable results, emphasizing the need for policies that balance enforcement with prevention and rehabilitation.
Experts recommend implementing the following key actions for lasting impact:
- Data-driven deployment: Utilize real-time crime data to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Community trust building: Foster transparent communication channels between law enforcement and residents.
- Economic opportunity programs: Support job creation and vocational training in high-crime areas.
- Focused intervention: Target repeat offenders with tailored rehabilitation and monitoring.
| Policy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Community Policing | Reduced violent confrontations |
| Youth Outreach Programs | Lower juvenile delinquency rates |
| Economic Initiatives | Increased employment, decreased incentives for crime |
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, a thorough examination of crime statistics reveals that the relationship between political leadership and crime rates in US cities is complex and cannot be reduced to simple partisan narratives. While Democrat-led cities often face unique socioeconomic challenges that impact public safety, attributing higher crime rates solely to political affiliation overlooks critical factors such as poverty, population density, and resource allocation. As discussions on crime and policy continue, a nuanced approach grounded in data, rather than political rhetoric, remains essential for informed public discourse.