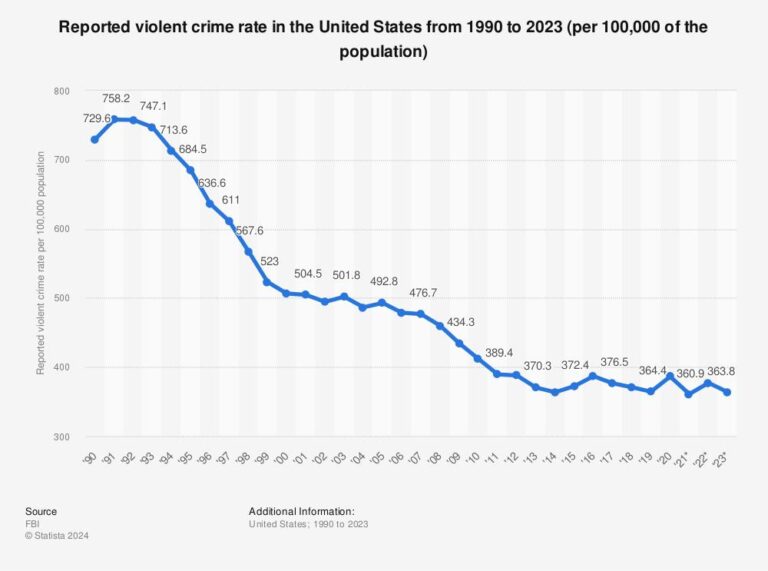
The reported violent crime rate in the United States has long been a critical indicator of public safety and social stability. According to data compiled by Statista, trends from 1990 through 2023 reveal significant shifts in the frequency and nature of violent offenses nationwide. This comprehensive overview examines how fluctuations in violent crime rates over the past three decades reflect broader societal changes, law enforcement strategies, and policy impacts, offering valuable insights into the evolving landscape of crime in America.
Trends in Violent Crime Rate Over Three Decades
Over the last three decades, the reported violent crime rate in the United States has shown notable fluctuations influenced by socio-economic changes, policy reforms, and law enforcement practices. The early 1990s marked a peak, with crime rates reaching historic highs. However, the mid-1990s witnessed a significant decline that persisted into the early 2000s, attributed largely to improved policing strategies, economic growth, and community-based initiatives targeting violence prevention.
Despite this overall downward trend, recent years have revealed a complex pattern with slight upticks in specific categories of violent crime, reflecting evolving challenges. Key observations include:
- Homicide rates have seen periods of increase in urban centers, raising concerns over gang-related violence.
- Aggravated assaults remain the most common violent crime, though rates fluctuate regionally.
- Rape and sexual assault reports have risen, influenced by greater awareness and reporting.
| Decade | Average Violent Crime Rate (per 100,000) | Trend |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | 750 | Sharp decline after peak |
| 2000s | 480 | Steady decrease |
| 2010s | 380 | Slower decline with fluctuations |
| 2020-2023 | 430 | Recent slight increase |
Regional Variations and Contributing Factors
Violent crime rates across the United States demonstrate marked differences between regions, influenced by a matrix of socioeconomic and demographic factors. Urban centers in the Northeast and West Coast often report higher incidences of violent crime per capita, which experts attribute to densely populated areas grappling with income inequality and social disenfranchisement. Conversely, many rural and suburban areas in the Midwest and South typically show lower violent crime rates, though this trend is not universal and exceptions persist, underscoring the complexity of regional dynamics.
Several key contributors play pivotal roles in shaping these regional disparities:
- Economic conditions: Regions with higher unemployment and poverty levels tend to experience elevated crime rates.
- Educational attainment: Areas with limited access to quality education often correlate with increased criminal activity.
- Policing strategies: Resource allocation and law enforcement presence vary widely, impacting crime deterrence effectiveness.
- Demographic shifts: Migration patterns and age distribution influence the social fabric and crime patterns.
- Legislative environment: Differences in state laws on firearms and criminal justice affect regional crime statistics.
| Region | Average Violent Crime Rate (per 100,000 inhabitants) | Key Contributing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 430 | Urban Density & Economic Disparity |
| South | 490 | Income Inequality & Firearm Accessibility |
| Midwest | 350 | Educational Attainment Levels |
| West | 480 | Demographic Changes & Policing Strategies |
Impact of Policy Changes on Crime Reduction
Shifts in criminal justice policies over the past three decades have played a pivotal role in the fluctuating rates of violent crime in the U.S. Legislative measures such as the 1994 Crime Bill, which increased funding for law enforcement and implemented harsher sentencing, coincided with a notable decline in crime rates during the late 1990s and early 2000s. However, recent reforms emphasizing rehabilitation over incarceration have shifted the focus towards reducing recidivism through community programs and mental health support. These policy adaptations reflect a broader strategy to address the root causes of crime rather than relying solely on punitive actions.
Data from several states highlight the variable impact of these policy changes. States that incorporated comprehensive reforms including improved police training, community engagement initiatives, and alternative sentencing for non-violent offenders experienced sharper decreases in violent crime rates. Below is a snapshot illustrating the comparative impact of key policies on violent crime reduction:
| Policy Initiative | Implementation Period | Average Crime Rate Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1994 Crime Bill Enforcement | 1995-2005 | 25% |
| Community Policing Programs | 2010-2020 | 18% |
| Rehabilitation & Mental Health | 2015-2023 | 12% |
| Alternative Sentencing Laws | 2018-2023 | 15% |
Strategies for Enhancing Community Safety and Prevention
Community safety initiatives rely heavily on a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes collaboration and proactive engagement. Law enforcement agencies partnering with local organizations and residents can foster trust and encourage community members to report suspicious activities without fear. Increased visibility through neighborhood patrols, use of technology such as surveillance cameras, and maintaining open lines of communication are essential components. Additionally, educational programs that address the root causes of crime — including poverty, lack of education, and unemployment — have proven effective in reducing violent incidents over time.
Key strategies that have demonstrated measurable impact include:
- Community Policing: Officers embedded within neighborhoods who build relationships and respond promptly to concerns.
- Youth Engagement Programs: Initiatives that offer mentorship, job training, and recreational activities to deter involvement in crime.
- Environmental Design: Improved street lighting, removal of abandoned properties, and maintenance of public spaces to reduce crime opportunities.
- Data-Driven Enforcement: Leveraging crime statistics to deploy resources strategically where violent incidents are most prevalent.
| Strategy | Primary Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Relationship Building | Reduced fear of crime by 30% |
| Youth Programs | Crime Prevention | Lowered youth violence by 25% |
| Environmental Design | Crime Opportunity Reduction | Decreased property crime by 15% |
Wrapping Up
In summary, the reported violent crime rate in the United States has experienced significant fluctuations from 1990 through 2023, reflecting the complex and evolving nature of public safety challenges. While periods of decline have offered some optimism, recent trends underscore the need for continued attention to crime prevention, law enforcement strategies, and community engagement. As policymakers and stakeholders analyze this extensive data, the pursuit of effective solutions remains critical to fostering safer communities nationwide.