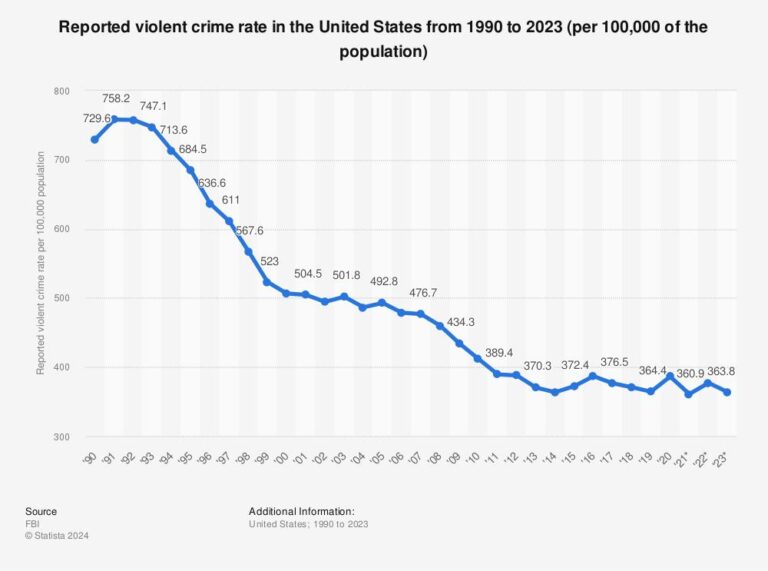
The latest data on reported violent crime rates across the United States in 2023 reveals significant variations from state to state, underscoring persistent regional disparities in public safety. According to Statista’s comprehensive report, certain states continue to grapple with higher incidences of violent offenses, while others show notable improvements or stability in crime rates. This detailed analysis provides crucial insights into the shifting landscape of violent crime nationwide, offering policymakers, law enforcement, and communities valuable information to address these challenges effectively.
Reported Violent Crime Rates Across U.S. States Highlight Regional Disparities
The latest data reveals pronounced differences in reported violent crime rates across the United States, underlining stark regional disparities. While some states grapple with higher incidences of offenses such as assault and robbery, others report notably lower figures, highlighting a complex landscape shaped by socioeconomic factors, legislative measures, and law enforcement efficacy. States in the South and some metropolitan areas continue to witness elevated rates, contrasting with parts of the Midwest and Northeast where numbers remain comparatively subdued.
Key factors contributing to this regional variation include:
- Economic disparities: Areas with higher poverty levels tend to experience more violent crime.
- Population density: Urban centers often report increased violent incidents due to larger, more concentrated populations.
- Law enforcement practices: Differences in policing strategies influence recorded crime statistics.
- Community programs: Investment in preventive initiatives correlates with reduced violence.
| Region | Average Violent Crime Rate (per 100,000 inhabitants) | Notable States |
|---|---|---|
| South | 550 | Louisiana, Alabama |
| West | 480 | California, Nevada |
| Midwest | 350 | Ohio, Minnesota |
| Northeast | 310 | New York, Massachusetts |
Deep Dive Into Contributing Factors Behind Rising and Falling Crime Trends
Several complex social dynamics are shaping the current shifts in violent crime rates across U.S. states. Economic disparities remain a principal driver, where regions experiencing higher unemployment and poverty often correspond with surges in violent offenses. Additionally, the availability and enforcement of gun control laws differ significantly by state, influencing the prevalence of firearm-related violence. Urbanization trends further compound this issue, as densely populated metropolitan areas frequently report higher crime incidents compared to rural counterparts. Community policing initiatives and local government interventions have also shown varying degrees of success in curbing violence, underscoring the importance of targeted strategies that address the unique challenges of each state.
Beyond socioeconomic elements, cultural and environmental factors contribute to fluctuating crime patterns. States with robust mental health services and education programs tend to experience declines in violent acts, highlighting prevention as a vital component. Conversely, states facing systemic inequalities and underfunded social infrastructures often contend with persistent crime problems. The following table encapsulates a snapshot of key factors correlating with rising and falling violent crime rates in select states for 2023:
| State | Economic Stability | Gun Law Strictness | Community Programs | Violent Crime Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | Medium | Strict | Extensive | Decreasing |
| Texas | Variable | Lenient | Moderate | Increasing |
| New York | High | Strict | Extensive | Decreasing |
| Florida | Medium | Lenient | Limited | Increasing |
- Economic Stability: Income inequality and job market strength affect crime rates.
- Gun Law Strictness: States with comprehensive regulations tend to have lower firearm violence.
- Community Programs: Local engagement and support services foster safer neighborhoods.
Impact of Violent Crime on Community Safety and Economic Stability
The rise in violent crime across various states has a cascading effect on both community cohesion and the broader economic landscape. High rates of violent offenses often erode residents’ sense of security, prompting increased expenditures on private security and community watch programs. Local businesses may face reduced customer footfall, impacting revenue and stunting growth opportunities. Moreover, neighborhoods with elevated violent crime frequently encounter challenges attracting new investments, leading to a persistent cycle of disinvestment and social decline.
Economically, violent crime imposes both direct and indirect costs. Medical expenses, property damage, and legal proceedings represent immediate financial strains, while long-term consequences — such as decreased property values and higher insurance premiums — burden communities extensively. Key factors influenced by elevated violent crime rates include:
- Business relocation: Companies opting for safer locales, leading to job losses.
- Housing market decline: Drop in property demand and rising vacancy rates.
- Public service strain: Increased policing and emergency response expenditures.
| State | Violent Crime Rate (per 100,000) | Estimated Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| California | 450 | $4.2 billion |
| Texas | 410 | $3.7 billion |
| Florida | 390 | $3.4 billion |
| Illinois | 420 | $3.8 billion |
Targeted Policy Recommendations to Address State-Level Crime Challenges
State governments face distinct challenges when tackling violent crime, requiring tailored strategies rather than one-size-fits-all solutions. In states with rising rates of firearm-related incidents, enhancing gun control laws and increasing community policing efforts have shown promise. Investments in mental health resources and social services also play a critical role in curbing violence by addressing root causes such as poverty and substance abuse. Meanwhile, states grappling with gang activity benefit from focused youth intervention programs and improved cooperation between local law enforcement and federal agencies.
Policymakers should prioritize data-driven approaches that consider the unique socio-economic factors in each region. For example, urban centers need expanded funding for crisis intervention teams and crime prevention through environmental design, while rural areas might see gains from improving law enforcement infrastructure and fostering local partnerships. Implementing these targeted measures can help balance public safety with community trust, ultimately steering down the violent crime trend nationwide.
Future Outlook
As the data from 2023 reveals, the reported violent crime rates across U.S. states continue to vary significantly, highlighting ongoing challenges and regional disparities in public safety. Understanding these patterns is crucial for policymakers, law enforcement, and communities as they develop targeted strategies to address and reduce violent crime. Continued monitoring and transparent reporting will play a vital role in shaping effective responses and fostering safer environments nationwide.