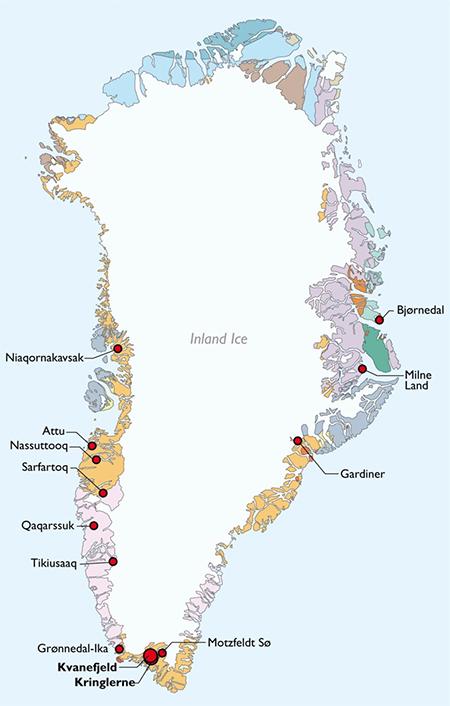
The US Export-Import Bank is reportedly weighing a $120 million loan to support a rare earth minerals project in Greenland, sources familiar with the matter told Reuters. The potential financing underscores Washington’s strategic push to secure critical mineral supplies amid growing competition with China. As Greenland holds vast deposits of rare earth elements essential for advanced technologies, the proposed loan signals increasing US interest in Arctic resources and efforts to bolster supply chains for clean energy and defense industries.
US Export-Import Bank Evaluates Significant Financial Support for Greenland Rare Earths Development
The US Export-Import Bank is actively assessing a potential $120 million loan aimed at boosting the development of a rare earths mining project in Greenland. This move underscores Washington’s strategic interest in securing critical minerals used in advanced technologies, ranging from electric vehicles to defense systems. The bank’s involvement signals a significant step in fostering U.S. access to essential resources while promoting economic cooperation with Greenland’s emerging mining sector.
Key aspects of the loan evaluation include:
- Financial viability and environmental sustainability of the Greenland project.
- Geopolitical advantages of expanding U.S. resource supply chains outside China.
- Long-term partnerships with Greenlandic authorities and mining companies.
| Loan Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Amount | $120 million |
| Focus | Rare earth mineral extraction and processing |
| Strategic Goal | Diversify U.S. mineral sourcing |
Strategic Implications of US Investment in Greenland’s Critical Minerals Sector
The potential $120 million loan from the US Export-Import Bank to support the Greenland rare earths project marks a pivotal moment in reinforcing America’s foothold in the critical minerals supply chain. This financing initiative is not merely an economic gesture; it underscores a calculated geopolitical maneuver aimed at reducing dependence on China for essential materials used in advanced technology and defense industries. By facilitating domestic access to rare earth minerals through Greenland’s untapped resources, the US is strategically positioning itself to safeguard supply resilience amid growing global competition.
Investment in Greenland’s critical minerals also carries implications beyond economics, reflecting broader security and diplomatic objectives. Key strategic benefits include:
- Enhanced supply chain security: Diversifying sourcing reduces vulnerabilities in technology manufacturing and military applications.
- Geopolitical leverage: Strengthening ties with Greenland boosts US influence in the Arctic, countering rival powers’ ambitions.
- Technological advancement: Access to rare earth elements supports innovation in clean energy, electronics, and defense systems.
| Parameter | US Strategic Focus | Greenland’s Role |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Security | Reduce reliance on China | Rich rare earth deposits |
| Geopolitical Position | Strengthen Arctic presence | Strategic location |
| Economic Impact | Create domestic industries | Potential new mineral economy |
Environmental and Community Considerations Surrounding the Greenland Rare Earths Project
As the Greenland Rare Earths Project progresses, significant attention has been directed toward its environmental impacts. The sensitive Arctic ecosystem faces risks from mining operations, including potential habitat disruption, water contamination, and carbon emissions. Local and international environmental groups have called for stringent safeguards to mitigate adverse effects, urging transparent environmental impact assessments and continuous monitoring throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Community engagement remains a cornerstone of the project’s development strategy. The project stakeholders have initiated consultations with indigenous Greenlandic communities to address their concerns regarding cultural preservation, employment opportunities, and economic benefits. These discussions aim to align the project’s goals with local needs, fostering trust and ensuring that the benefits extend beyond mere resource extraction.
- Protection of Arctic flora and fauna
- Implementation of water management systems
- Local job creation and skills training
- Incorporation of traditional knowledge in planning
Recommendations for Enhancing Transparency and Stakeholder Engagement in Loan Approval Process
To foster greater confidence and accountability in significant financial decisions, it is imperative to implement clear communication strategies that outline each stage of the loan approval. This includes publishing detailed timelines, criteria, and stakeholder responsibilities. Publicly accessible platforms where stakeholders can track progress in real time would minimize uncertainty and misinformation. Moreover, embracing digital tools such as interactive dashboards and community portals can facilitate dialogue and ensure that voices from local communities potentially impacted by the Greenland rare earths project are actively heard and integrated.
Equally important is involving a diverse group of stakeholders early in the decision-making process. This can be achieved through:
- Regular public consultations and workshops to discuss environmental and economic implications
- Transparent reporting on environmental and social risk assessments, accessible to both experts and the general public
- Independent third-party audits to validate data and ensure compliance with ethical standards
- Inclusive feedback mechanisms that allow for concerns and suggestions to be formally recorded and addressed.
The Conclusion
As the US Export-Import Bank weighs a $120 million loan to support Greenland’s rare earths project, the move signals Washington’s strategic intent to secure critical mineral supplies amid intensifying global competition. Stakeholders will be closely watching how this potential financing shapes the future of rare earths development in the Arctic region and the broader geopolitical landscape influencing resource access. Further updates are expected as negotiations progress and regulatory reviews take shape.