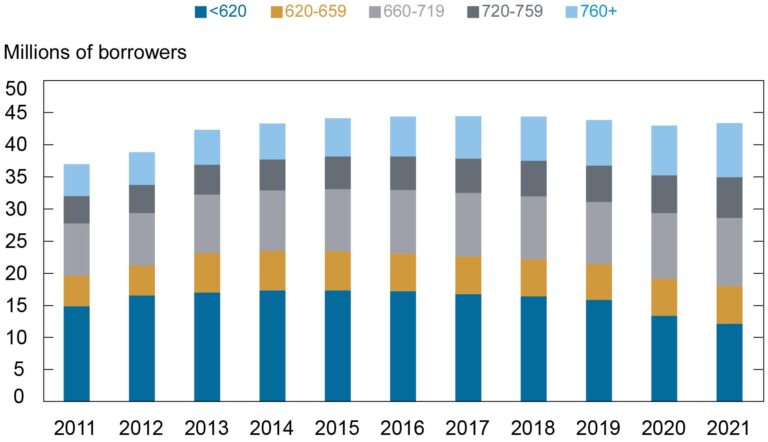
Significant reforms to the student loan system have moved closer to becoming law, marking a crucial development for millions of borrowers nationwide. The latest legislative progress, reported by USA Today, signals potential changes that could reshape repayment options, forgiveness programs, and financial relief measures. As lawmakers advance these proposals, students and graduates are watching closely, hopeful for relief amid soaring education costs and mounting debt.
Major Student Loan Reforms Advance in Legislative Process
In a significant move toward alleviating the financial burden on millions of Americans, key provisions aimed at overhauling the student loan system have successfully passed a critical legislative milestone. Lawmakers have reached a consensus on measures that promise to simplify repayment options, increase borrower protections, and introduce income-driven plans that adapt more flexibly to individual circumstances. These changes are designed to provide relief and predictability for those struggling to manage their student debt in an increasingly challenging economic environment.
The proposed reforms include several impactful components, primarily focused on:
- Streamlined repayment plans that adjust monthly payments based on borrowers’ current income and family size.
- Expanded loan forgiveness programs targeting low-income and public service employees.
- Improved transparency in loan servicing to reduce hidden fees and confusing terms.
| Feature | Current Policy | Proposed Change |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment Cap | 10-15% of discretionary income | 5-10%, with annual recalculations |
| Loan Forgiveness Timeframe | 20-25 years | 10-15 years for qualifying careers |
| Servicer Accountability | Minimal regulatory oversight | Enhanced monitoring and penalties |
Key Provisions and Their Impact on Borrowers Explored
The new student loan legislation introduces several game-changing provisions designed to ease the financial burden on millions of borrowers across the country. Among the most significant changes is the expansion of income-driven repayment plans, which now offer lower monthly payments based on a wider range of income thresholds. This shift aims to reduce defaults and improve long-term repayment success by aligning payment amounts more closely with borrowers’ actual income.
Additionally, the bill proposes enhanced loan forgiveness options for public service workers, educators, and low-income borrowers, potentially wiping out decades of debt for many. The introduction of stricter regulations on private loan servicers ensures greater transparency and accountability, promising borrowers clearer communication and streamlined processes. Below is a snapshot of the core provisions and their anticipated impact on borrowers:
| Provision | Impact |
|---|---|
| Expanded Income-Driven Repayment | Lower monthly payments; broader eligibility |
| Public Service Loan Forgiveness Enhancement | Faster forgiveness for qualifying borrowers |
| Private Loan Servicer Regulations | Greater transparency and borrower protections |
| Debt Relief for Low-Income Borrowers | Targeted forgiveness and reduced interest accumulation |
- Increased flexibility in repayment terms fosters financial stability
- Broader support for public servants encourages retention in critical jobs
- Enhanced oversight regulates predatory lending practices
Expert Analysis on Eligibility and Payment Adjustments
Under the latest legislative updates, eligibility criteria for student loan relief programs have been refined, prioritizing borrowers based on income thresholds and repayment history. Experts highlight that this adjustment aims to better target aid to those most affected by economic downturns, while discouraging defaults through stricter qualification checks. Key elements of the revised eligibility include:
- Income verification: Borrowers must provide recent tax documents to confirm eligibility annually.
- Repayment consistency: Preference given to those with a record of timely payments over the past 12 months.
- Loan type restrictions: Only federal student loans qualify, excluding private and commercial debt.
The payment adjustment framework introduces a tiered system to accommodate diverse financial situations, replacing a one-size-fits-all model. According to financial analysts, this nuanced approach could significantly reduce default rates and encourage sustainable repayment plans. Below is a simplified breakdown of the proposed payment adjustment tiers:
| Income Level | Monthly Payment Rate | Adjustment Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Below $30,000 | 5% of discretionary income | Lowest tier; extended grace periods available |
| $30,000 – $60,000 | 10% of discretionary income | Standard repayment schedule applies |
| Above $60,000 | 15% of discretionary income | Accelerated payment with lower interest rates |
Navigating the New Rules How Borrowers Should Prepare
The recent legislative strides signal significant shifts for borrowers, demanding proactive steps to secure favorable outcomes. Experts recommend reviewing current loan terms immediately, as updated regulations could alter repayment schedules, interest rates, and forgiveness eligibility. Keeping meticulous records and staying informed about new deadlines will be essential to avoid costly oversights.
Here are key actions borrowers should consider:
- Verify loan balances and servicer information to ensure accuracy as changes roll out.
- Explore income-driven repayment options newly expanded under the updated provisions.
- Assess eligibility for forgiveness programs potentially broadened in scope.
| Loan Status | Action Step | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| In Repayment | Update repayment plan | Within 60 days |
| Deferment or Forbearance | Confirm eligibility expiration | Within 90 days |
| Defaulted | Contact servicer to rehabilitate | Before new law takes effect |
The Way Forward
As the legislative process moves forward, these significant student loan reforms are poised to reshape the financial landscape for millions of borrowers across the country. Stakeholders and borrowers alike will be watching closely as lawmakers continue to debate the proposals that could offer much-needed relief and make higher education more accessible. The coming weeks will be critical in determining whether these changes become permanent fixtures in the nation’s approach to student debt.