Analyzing Arrest Trends in the U.S.: A Comprehensive Review from 1990 to 2023
Transformations in Arrest Patterns: Reflecting Shifts in Crime and Society
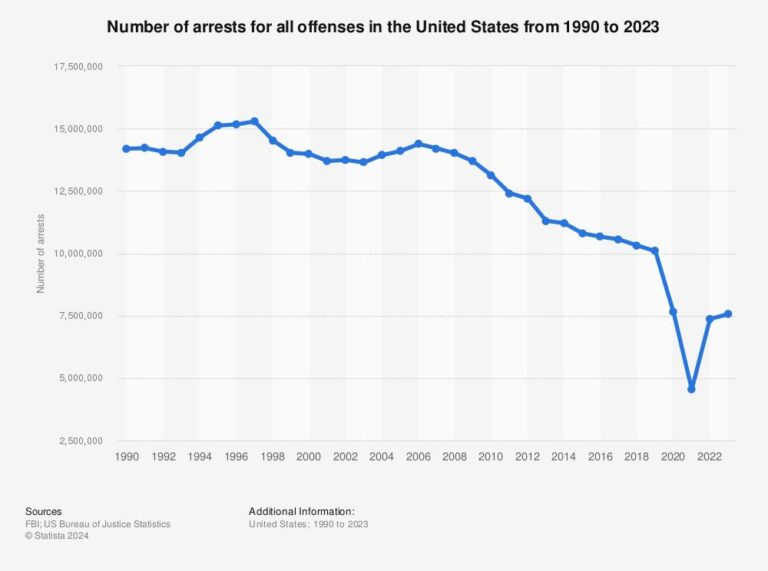
Over the past three decades, arrest data in the United States has undergone significant changes, mirroring broader societal shifts and evolving law enforcement methodologies. The 1990s were characterized by a sharp rise in arrests, predominantly driven by stringent crackdowns on drug-related offenses and violent crimes. Entering the 2000s, arrest figures began to level off and then slowly declined, influenced by reforms in the criminal justice system, advancements in forensic and surveillance technologies, and changing public attitudes toward policing. The 2010s saw a notable uptick in arrests linked to cyber offenses and financial fraud, underscoring the growing impact of digital crime. More recently, from 2020 through 2023, arrest trends have been shaped by the socio-economic upheavals caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, affecting various crime categories in complex ways.
- 1990s: Sharp increase in arrests for drug and violent offenses
- 2000s: Stabilization followed by gradual decline in total arrests
- 2010s: Growth in cybercrime and white-collar crime arrests
- 2020-2023: Arrest fluctuations influenced by pandemic and economic stressors
| Decade | Approximate Arrests (Millions) | Predominant Crime Categories |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | 15.2 | Drug and Violent Crimes |
| 2000s | 14.0 | Drug and Property Crimes |
| 2010s | 12.3 | Cyber and Financial Crimes |
| 2020-2023 | 11.1 | Varied Offenses, Pandemic Impact |
Economic and Social Drivers Behind Arrest Rate Fluctuations
The trajectory of arrest rates over the last thirty years closely aligns with the nation’s economic and social conditions. Periods marked by economic downturns and rising unemployment often correspond with spikes in arrests, especially in urban centers where poverty is more concentrated. These hardships tend to increase the prevalence of crimes linked to economic necessity and petty offenses. Additionally, systemic inequalities such as limited educational opportunities and insufficient social support exacerbate these issues, disproportionately impacting disadvantaged populations and contributing to higher arrest rates.
- Economic inequality and concentrated poverty zones
- Youth unemployment and labor market volatility
- Educational disparities and dropout prevalence
- Access to social welfare and community programs
| Timeframe | Unemployment Rate (%) | Average Arrest Rate (per 100,000 residents) |
|---|---|---|
| 1990-1999 | 5.2 | 4,500 |
| 2000-2009 | 6.1 | 4,700 |
| 2010-2019 | 5.3 | 4,300 |
| 2020-2023 | 6.8 | 4,600 |
These statistics underscore the cyclical relationship between economic challenges and crime rates, highlighting the critical need for policies that tackle underlying social inequities. Expanding job opportunities and improving educational access are pivotal strategies for lowering arrest rates and enhancing community well-being.
Evolution of Policing: What Arrest Data Reveals About Law Enforcement Practices
Examining arrest records over time offers valuable insights into how policing tactics have evolved in response to shifting crime trends. For example, surges in drug-related arrests often coincide with intensified enforcement efforts and strict drug policies. On the other hand, declines in property crime arrests have been associated with the rise of community-oriented policing and the deployment of innovative crime prevention technologies. This dynamic adaptation highlights the importance of balancing proactive crime control with the protection of civil liberties.
- Impact of legislative changes, including decriminalization and sentencing reforms
- Ongoing concerns about racial and demographic disparities in arrests
- Increased focus on combating cybercrime as digital offenses rise
| Year | Total Arrests | Percentage for Drug Offenses | Percentage for Property Crimes | Percentage for Violent Crimes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 14,500,000 | 35% | 40% | 25% |
| 2005 | 13,200,000 | 39% | 34% | 27% |
| 2015 | 11,800,000 | 42% | 30% | 28% |
| 2023 | 10,500,000 | 45% | 25% | 30% |
Policy Strategies for Lowering Arrest Rates and Strengthening Community Safety
Effectively addressing the persistent challenges revealed by arrest data demands a proactive, community-focused policy framework. Investing in education, mental health services, and vocational training has proven to reduce risk factors associated with criminal conduct. Law enforcement agencies are increasingly leveraging data-driven approaches to allocate resources efficiently, targeting high-risk areas while promoting transparency and accountability. Enhancing community policing efforts remains crucial for fostering trust and collaboration between law enforcement and residents, which is essential for long-term crime reduction.
Additional reforms include revising sentencing guidelines to reduce incarceration for non-violent offenses and expanding diversion programs that prioritize rehabilitation over punishment. Key policy recommendations include:
- Expanding access to affordable mental health and addiction treatment services.
- Implementing restorative justice models to repair harm and lower repeat offenses.
- Increasing funding for youth engagement and development programs.
- Promoting transparency through body cameras and independent oversight mechanisms.
- Reforming bail and sentencing policies to reduce unnecessary pretrial detention.
| Policy Area | Expected Impact | Projected Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Enhanced public trust and decreased arrest rates | Short to Medium Term |
| Sentencing Reform | Lower incarceration rates | Medium to Long Term |
| Youth Development Initiatives | Reduced juvenile delinquency | Long Term |
Conclusion: Leveraging Arrest Data to Inform Future Justice Policies
The extensive arrest data from 1990 through 2023 offers critical insights into the evolving nature of crime and law enforcement in the United States. These trends not only reflect changes in criminal activity and policing strategies but also serve as a foundation for policymakers, law enforcement officials, and communities aiming to enhance public safety. As social conditions and legal frameworks continue to shift, ongoing analysis of arrest patterns remains vital for developing balanced, effective policies that uphold justice, equity, and security.