The U.S. Department of Education, a key federal agency responsible for shaping American education policy and administering funding programs, has long been a focal point of political debate. With a sizable budget and a workforce dedicated to improving educational outcomes nationwide, the agency plays a critical role in supporting schools, students, and educators. However, during his presidency, Donald Trump repeatedly called for the department’s elimination, arguing that it represented unnecessary federal overreach. This article examines the Department of Education’s budget and staffing, alongside the rationale behind Trump’s push to shutter the agency, as reported by Reuters.
US Department of Education Budget Breakdown Reveals Priorities and Spending Challenges
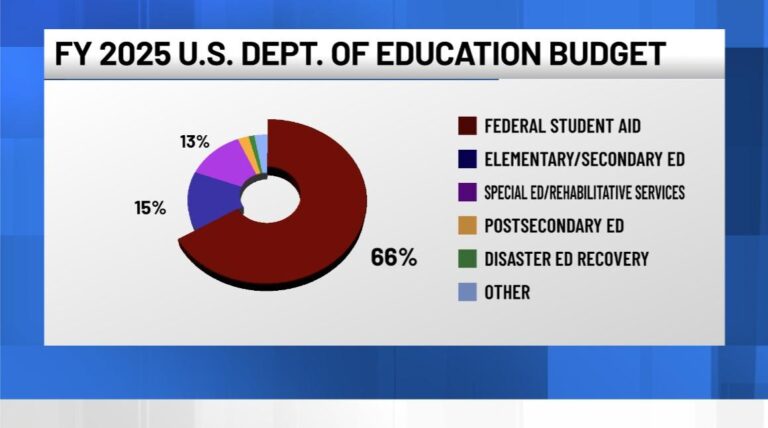
The latest budget proposal for the US Department of Education highlights a clear emphasis on enhancing K-12 education, expanding access to higher education, and investing in student financial aid programs. A significant portion of the funding is allocated to grants for STEM initiatives and support for low-income and minority students. This allocation underscores the administration’s commitment to closing achievement gaps and boosting workforce readiness through targeted educational programs.
Key budget priorities include:
- Increased funding for Title I programs targeting disadvantaged schools
- Expanded Pell Grants to make college more affordable
- Innovative workforce development partnerships with private sectors
- Support for special education and early childhood programs
| Department Area | Budget Allocation (Billion $) | Percentage of Total Budget |
|---|---|---|
| K-12 Education | 40 | 45% |
| Higher Education | 30 | 34% |
| Student Aid & Grants | 15 | 17% |
| Administrative Costs | 3 | 4% |
Despite these priorities, the Department faces ongoing challenges, including growing concerns about administrative overhead and the efficiency of fund allocation. Critics argue that a sizable portion of the budget is consumed by bureaucratic expenses rather than direct educational impact. Furthermore, ideological divides have led to calls from some political figures, notably former President Trump, to dismantle or radically restructure the Department, citing inefficiencies and advocating for state-level control instead.
The debate around the Department’s role continues to fuel budget scrutiny, with stakeholders pushing for reforms that would optimize resource distribution and prioritize classroom needs over administrative layers. This battle between federal oversight and local autonomy remains central to discussions on the future of US education funding.
Workforce Analysis Highlights Staffing Levels and Key Roles Within the Department
The US Department of Education employs approximately 4,400 staff members across various divisions, including policy development, grants management, and enforcement of federal education laws. These employees are primarily concentrated in Washington D.C., with a significant number also working in regional offices nationwide. Among the top roles are education analysts, program managers, compliance officers, and administrative support personnel who ensure the smooth functioning of the department’s numerous initiatives.
Key staffing statistics reveal a trend toward specialization:
- Policy and Planning: 28% of workforce, focusing on legislation and federal guidance.
- Grant Administration: 25%, handling distribution and oversight of federal funding.
- Compliance and Enforcement: 20%, responsible for monitoring adherence to federal regulations.
- Support Services: 27%, providing essential logistical and clerical assistance.
These divisions collaborate closely to implement education programs aligned with federal objectives, but they also represent areas targeted for budget cuts and restructuring under the current political climate.
| Department Area | Percentage of Workforce |
|---|---|
| Policy and Planning | 28% |
| Grant Administration | 25% |
| Compliance and Enforcement | 20% |
| Support Services | 27% |
Examining Former President Trump’s Rationale Behind Proposing the Department’s Closure
Former President Trump’s push to dismantle the Department of Education was anchored in his administration’s broader agenda of reducing federal oversight and promoting state-level autonomy in education policy. He argued that the department’s existence led to excessive bureaucracy, inefficiencies, and unnecessary federal spending, which, in his view, did not translate into measurable improvements in student outcomes. Trump’s plan aimed to redirect authority to state and local governments, fostering competition among schools and encouraging innovation free from federal mandates.
Key points from Trump’s rationale included:
- Belief that the department imposes one-size-fits-all regulations detrimental to diverse educational needs.
- Concerns over the department’s budget, highlighting that funds could be better utilized directly within classrooms.
- Criticism of the federal student loan system’s complexity and the department’s role in perpetuating it.
- Promotion of school choice initiatives such as charter schools and vouchers as superior alternatives.
| Department Aspect | Trump’s Critique | Intended Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Budget Utilization | Overspending & inefficiency | Streamline spending, increase classroom funding |
| Federal Oversight | Excessive centralized control | Empower states with more autonomy |
| Student Loans | Complexity and federal entanglement | Simplify system, reduce federal involvement |
| Educational Innovation | Restricted by broad mandates | Encourage competition and choice |
Recommendations for Future Policy Adjustments and Departmental Efficiency Improvements
To enhance both fiscal responsibility and departmental effectiveness, policymakers should consider re-evaluating the allocation of funds with a focus on programs demonstrating clear, data-backed results in improving educational outcomes. Streamlining grant management processes and increasing transparency in budget reporting could address concerns about inefficiencies and misuse of resources. Additionally, a shift towards more localized decision-making might empower school districts and reduce bureaucratic delays, fostering innovation at the ground level.
Improving employee productivity through targeted training and optimizing workforce size based on essential roles would also trim unnecessary overhead. Introducing performance metrics linked to specific educational goals can help identify underperforming projects and personnel, while encouraging a culture of accountability. Examples of recommended adjustments include:
- Implementing a transparent, results-driven budgeting model prioritizing underserved communities.
- Enhancing digital infrastructure to facilitate remote learning and administrative efficiency.
- Regular audits and public performance reports to ensure taxpayer funds are maximized.
- Reorganizing teams around strategic initiatives rather than legacy divisions.
| Focus Area | Proposed Adjustment | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Budget Allocation | Shift to evidence-based grants | Improved outcome accountability |
| Workforce Efficiency | Performance-based evaluations | Higher staff productivity |
| Technology Use | Upgrade digital tools & platforms | Enhanced remote access & efficiency |
In Summary
In conclusion, the US Department of Education remains a focal point in the ongoing debates over federal spending and government priorities. With a substantial budget and a workforce committed to managing educational programs nationwide, the agency plays a critical role in shaping American education policy. However, as reflected in former President Trump’s calls to shut down the department, questions persist about the federal government’s role in education and the allocation of taxpayer dollars. As policymakers continue to grapple with these issues, the future of the Department of Education will likely remain a contentious topic in the national discourse.